Insulin resistance - what is it? Analysis and treatment of diabetes mellitus. Insulin resistance syndrome: causes, symptoms, treatment.
Different people are characterized by a different ability of insulin to stimulate the absorption of glucose. It is important to know that a person may have normal sensitivity to one or more of the effects of this compound and at the same time be completely resistant to others. Next, we will analyze the concept of "insulin resistance": what it is, how it manifests itself.
General information
Before analyzing the concept of "insulin resistance", what it is and what signs it has, it should be said that this disorder is quite common. More than 50% of people with hypertension suffer from this pathology. Most often, insulin resistance (what it is, will be described below) is found in the elderly. But in some cases it comes to light and in the childhood. The syndrome of insulin resistance often remains unrecognized until metabolic disorders begin to appear. The risk group includes persons with dyslipidemia or impaired glucose tolerance, obesity, hypertension.
insulin resistance
What it is? What are the features of the violation? insulin resistance is an incorrect response of the body to the action of one of the compounds. The concept is applicable to different biological effects. This, in particular, refers to the effect of insulin on protein and gene expression, and the function of the vascular endothelium. The disturbed response leads to an increase in the concentration of the compound in the blood relative to that required for the available amount of glucose. Insulin resistance syndrome is a combined disorder. It involves changes in glucose tolerance, type 2 diabetes, dyslipidemia, and obesity. "Syndrome X" also implies resistance to glucose uptake (insulin-dependent). 
Development mechanism
To date, experts have not been able to fully study it. Disorders that lead to the development of insulin resistance can occur at the following levels:
- Receptor. In this case, the condition is manifested by affinity or a decrease in the number of receptors.
- At the level of glucose transport. In this case, a decrease in the number of GLUT4 molecules is revealed.
- Prereceptor. In this case, we talk about abnormal insulin.
- Post-receptor. In this case, there is a violation of phosphorylation and a violation of signal transmission.
Anomalies of insulin molecules are quite rare and do not have clinical significance. Receptor density may be reduced in patients due to negative feedback. It is caused by hyperinsulinemia. Often, patients have a moderate decrease in the number of receptors. In this case, the level of feedback is not considered a criterion by which the degree of insulin resistance is determined. The causes of the disorder are reduced by experts to post-receptor signal transduction disorders. Provoking factors, in particular, include:
- Smoking.
- Increase in the content of TNF-alpha.
- Decrease in physical activity.
- Increasing the concentration of non-esterified fatty acids.
- Age.

These are the main factors that more often than others can provoke insulin resistance. Treatment includes the use of:
- Diuretics of the thiazide group.
- nicotinic acid.
- Corticosteroids.
Increased insulin resistance
Influence on glucose metabolism occurs in adipose tissue, muscles and liver. Skeletal muscle metabolizes approximately 80% of this compound. Muscles in this case act as an important source of insulin resistance. Glucose is taken up into cells by a special transport protein, GLUT4. Activation of the insulin receptor triggers a series of phosphorylation reactions. They eventually lead to the translocation of GLUT4 to cell membrane from the cytosol. This allows glucose to enter the cell. Insulin resistance (the norm will be indicated below) is caused by a decrease in the degree of GLUT4 translocation. At the same time, there is a decrease in the use and uptake of glucose by cells. Along with this, in addition to facilitating glucose uptake in peripheral tissues, hyperinsulinemia suppresses the production of glucose by the liver. With type 2 diabetes, it resumes.
Obesity
It is combined with insulin resistance quite often. When the patient exceeds the weight by 35-40%, the sensitivity decreases by 40%. The one located in the anterior abdominal wall has a higher metabolic activity than the one located below. In the course of medical observations, it has been established that increased release of fatty acids from abdominal fibers into the portal bloodstream provokes the production of triglycerides by the liver. 
Clinical signs
Insulin resistance, the symptoms of which are predominantly metabolically related, may be suspected in patients with abdominal obesity, gestational diabetes, a family history of type 2 diabetes, dyslipidemia, and hypertension. At risk and women with PCOS (polycystic ovaries). Due to the fact that obesity is a marker of insulin resistance, it is necessary to assess the nature of the distribution of fatty tissue. Its location can be gynecoid - in the lower part of the body, or android type - in the anterior wall of the peritoneum. Upper body accumulation is a more significant predictor of insulin resistance, altered glucose tolerance, and DM than lower body obesity. To determine the amount of abdominal fat, you can use the following method: determine the ratio of waist, hips and BMI. With indicators of 0.8 for women and 0.1 for men and a BMI greater than 27, abdominal obesity and insulin resistance are diagnosed. Symptoms of pathology are also manifested externally. In particular, wrinkled, rough hyperpigmented areas are noted on the skin. Most often they appear in the armpits, on the elbows, under the mammary glands. The analysis for insulin resistance is a calculation according to the formula. HOMA-IR is calculated as follows: fasting insulin (µU/mL) x fasting glucose (mmol/L). The result obtained is divided by 22.5. The result is an index of insulin resistance. Norma -<2,77. При отклонении в сторону увеличения может диагностироваться расстройство чувствительности тканей. 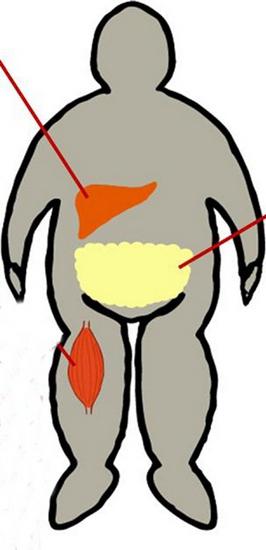
Violations of the activity of other systems: vascular atherosclerosis
Today, there is no single explanation of the mechanism of the influence of insulin resistance on the damage to the cardiovascular system. There may be a direct effect on atherogenesis. It is caused by the ability of insulin to stimulate lipid synthesis and the proliferation of smooth muscle components in the vascular wall. At the same time, atherosclerosis can be caused by concomitant metabolic disorders. For example, it can be hypertension, dyslipidemia, changes in glucose tolerance. In the pathogenesis of the disease, the impaired function of the vascular endothelium is of particular importance. Its task is to maintain the tone of the blood channels due to the secretion of mediators of vasodilation and vasoconstriction. In the state, it provokes relaxation of the smooth muscle fibers of the vascular wall with the release of nitric oxide (2). At the same time, its ability to enhance endothelium-dependent vasodilation changes significantly in obese patients. The same applies to patients with insulin resistance. With the development of the inability of the coronary arteries to respond to normal stimuli and expand, we can speak of the first stage of microcirculation disorders - microangiopathy. This pathological condition is observed in most patients with DM (diabetes mellitus).

Insulin resistance can provoke atherosclerosis through disturbances in the process of fibrinolysis. PAI-1 (plasminogen activator inhibitor) is found in high concentrations in diabetic and obese patients without diabetes. The synthesis of PAI-1 is stimulated by proinsulin and insulin. The level of fibrinogen and other procoagulant factors is also increased.
Altered glucose tolerance and type 2 diabetes
Insulin resistance is a precursor to the clinical manifestation of DM. Beta cells in the pancreas are responsible for lowering glucose levels. The decrease in concentration is carried out by increasing the production of insulin, which, in turn, leads to relative hyperinsulinemia. Euglycemia can persist in patients for as long as the beta cells are able to maintain a sufficiently high plasma insulin level to overcome resistance. Ultimately, this ability is lost, and the concentration of glucose increases significantly. The key factor responsible for fasting hyperglycemia in T2DM is hepatic insulin resistance. The healthy response is to lower glucose production. With insulin resistance, this reaction is lost. As a result, the liver continues to overproduce glucose, leading to fasting hyperglycemia. With the loss of the ability of beta cells to provide hypersecretion of insulin, there is a transition from insulin resistance with hyperinsulinemia to altered glucose tolerance. Subsequently, the condition is transformed into clinical diabetes and hyperglycemia.
hypertension
There are several mechanisms that cause its development against the background of insulin resistance. As observations show, the weakening of vasodilation and the activation of vasoconstriction can contribute to an increase in vascular resistance. Insulin stimulates the nervous (sympathetic) system. This leads to an increase in the plasma concentration of norepinephrine. Patients with insulin resistance have an increased response to angiotensin. In addition, the mechanisms of vasodilation may be disturbed. In a normal state, the introduction of insulin provokes relaxation of the muscular vascular wall. Vasodilation in this case is mediated by the release/production of nitric oxide from the endothelium. In patients with insulin resistance, endothelial function is impaired. This leads to a decrease in vasodilation by 40-50%. 
Dyslipidemia
With insulin resistance, the normal suppression of the release of free fatty acids after eating from adipose tissue is disrupted. The increased concentration forms a substrate for enhanced triglyceride synthesis. This is an important step in the production of VLDL. With hyperinsulinemia, the activity of an important enzyme, lipoprotein lipase, decreases. Among the qualitative changes in the spectrum of LDL against the background of type 2 diabetes and insulin resistance, an increased degree of oxidation of LDL particles should be noted. Glycated apolipoproteins are considered to be more susceptible to this process.
Therapeutic activities
Insulin sensitivity can be improved in several ways. Of particular importance is weight loss and physical activity. Diet is also important for people diagnosed with insulin resistance. The diet helps to stabilize the condition within a few days. Increased sensitivity will further contribute to weight loss. For people who have established insulin resistance, treatment consists of several stages. Stabilization of diet and physical activity is considered the first stage of therapy. For people who have insulin resistance, the diet should be low in calories. A moderate decrease in body weight (by 5-10 kilograms) often improves glucose control. Calories are 80-90% distributed between carbohydrates and fats, 10-20% are proteins.
Medications
Means "Metamorphine" refers to medicines of the group of biguanides. The drug helps to increase peripheral and hepatic sensitivity to insulin. In this case, the agent does not affect its secretion. In the absence of insulin, Metamorphin is ineffective. Troglitazone is the first thiazolidinedione drug to be approved for use in the United States. The drug enhances the transport of glucose. This is probably due to the activation of the PPAR-gamma receptor. And due to this, the expression of GLUT4 is enhanced, which, in turn, leads to an increase in insulin-induced glucose uptake. For patients who have insulin resistance, treatment can be prescribed and combined. The above agents may be used in combination with a sulfonylurea, and sometimes with each other to obtain plasma glucose and other disorders. The drug "Metamorphine" in combination with a sulfonylurea enhances the secretion and sensitivity to insulin. At the same time, glucose levels decrease after meals and on an empty stomach. In patients who were prescribed combined treatment, manifestations of hypoglycemia were more often observed.
Insulin resistance is a violation of the interaction of incoming insulin on tissues. In this case, insulin can come both naturally from the pancreas, and through the introduction of an injection of the hormone.
The hormone, in turn, is involved in metabolism, growth and reproduction of tissue cells, DNA synthesis and gene transcription.
In modern times, insulin resistance is associated not only with metabolic disorders and an increased risk of type 2 diabetes. Including insulin resistance negatively affects the metabolism of fats and proteins, gene expression.
Including insulin resistance will disrupt the functionality of endothelial cells, which are the inner layer on the walls of blood vessels. As a result, the violation leads to vasoconstriction and the development of atherosclerosis.
Diagnosis of insulin resistance
The disorder is detected if the patient has symptoms of the metabolic syndrome. Signs such as fat deposits in the waist area, high blood pressure, poor blood tests for triglycerides and cholesterol may be present. Including such a phenomenon is diagnosed if the patient's analysis showed an increased protein in the urine.
Diagnosis of insulin resistance is carried out primarily through tests that must be taken regularly. However, due to the fact that the level of insulin in the blood plasma can change, diagnosing such a disease is very difficult.
If the tests were performed on an empty stomach, the norm of insulin levels in the blood plasma is 3-28 mcU / ml. If insulin in the blood is elevated and exceeds the specified rate, the patient has hyperinsulinism.
The reasons for the fact that insulin in the blood is too high may be due to the fact that the pancreas produces an excess amount of it in order to compensate for the insulin resistance of tissues.
Such an analysis may indicate that the patient may develop type 2 diabetes or cardiovascular disease.
To accurately identify the disorder, a hyperinsulinemic insulin clamp is performed. This laboratory method consists of continuous intravenous administration of insulin and glucose for four to six hours.
Such diagnostics is very time-consuming, so it is used quite rarely. Instead, a blood test is done on an empty stomach to check for plasma insulin levels.
As it turned out in the course of research, this violation can most often occur:
- In 10 percent of cases without any metabolic disorders;
- In 58 percent of cases, if there are symptoms of high blood pressure over 160/95 mm Hg. Art.;
- In 63 percent of cases with hyperuricemia, when serum uric acid levels are above 416 µmol/liter in men and 387 µmol/liter in women;
- In 84 percent of cases with an increase in the level of fat cells, when triglycerides are above 2.85 mmol / liter;
- In 88 percent of cases with a low level of positive cholesterol, when its indicators are less than 0.9 mmol / liter in men and 1.0 mmol / liter in women;
- In 84 percent of cases, if there are symptoms of the development of type 2 diabetes;
- In 66 percent of cases with impaired glucose tolerance.
The HOMA Insulin Resistance Index is used to determine whether there is insulin resistance. After the analysis of the level of insulin and fasting glucose is passed, the calculation of the HOMA index is carried out.
With an increase in the level of fasting insulin or glucose, the HOMA index also increases. For example, if the analysis showed the level of glycemia on an empty stomach 7.2 mmol / liter, and insulin 18 mcU / ml, the HOMA index is 5.76. Insulin levels are considered normal if the HOMA index is less than 2.7.
Regulation of metabolism with insulin
Insulin allows you to activate metabolic processes such as glucose transport and glycogen synthesis. This hormone is also responsible for DNA synthesis.
Insulin provides:
- Glucose uptake by muscle, liver and adipose tissue cells;
- Synthesis of glycogen in the liver;
- Capture by cells of amino acids;
- DNA synthesis;
- Protein formation;
- The formation of fatty acids;
- transport of ions.
Insulin also helps prevent unwanted symptoms such as:
- The breakdown of adipose tissue and the entry of fatty acids into the blood;
- The transformation of glycogen in the liver and the entry of glucose into the blood;
- cell self-destruction.
It is important to understand that the hormone does not allow fat tissues to break down. Because of this reason, if insulin resistance is observed and insulin levels are elevated, it is almost impossible to reduce excess weight.
The degree of sensitivity to insulin of different tissues of the body
In the treatment of certain diseases, insulin sensitivity of muscle and adipose tissues is primarily considered. Meanwhile, these tissues have different insulin resistance.
So, to suppress the breakdown of fats in tissues, no more than 10 mcU / ml of insulin in the blood is required. At the same time, to suppress the entry of glucose from the liver into the blood, approximately 30 μU / ml of insulin is needed. To increase the uptake of glucose by muscle tissues, you need 100 mcU / ml or more of the hormone in the blood.
Tissues lose sensitivity to insulin due to genetic predisposition and unhealthy lifestyle.
At a time when the pancreas begins to fail to cope with the increased load, the patient develops type 2 diabetes mellitus. If insulin resistance syndrome is treated early, many complications can be avoided.
It is important to understand that insulin resistance can occur in people who do not have metabolic syndrome. In particular, resistance is diagnosed in people with:
- polycystic ovaries in women;
- chronic renal failure;
- infectious diseases;
- glucocorticoid therapy.
Including insulin resistance in some cases is diagnosed in women during pregnancy, but after the birth of a child, this condition usually disappears.
Also, resistance can increase with age, therefore, on what kind of lifestyle a person leads. It depends whether he will suffer from type 2 diabetes mellitus in old age or have problems in the cardiovascular system.
Why Type 2 Diabetes Develops
The causes of diabetes mellitus lie directly in the insulin resistance of muscle, adipose tissue and liver cells. Due to the fact that the body becomes less sensitive to insulin, less glucose enters the muscle cells. The active breakdown of glycogen to glucose and the production of glucose from amino acids and other raw materials begins in the liver.
With insulin resistance of adipose tissues, the anti-lipolytic effect of insulin weakens. Initially, this process is compensated by increased production of insulin from the pancreas.
Late in the disease, body fat begins to break down into glycerol and free fatty acids.
These substances after entering the liver are converted into very dense lipoproteins. This unhealthy substance is deposited on the walls of blood vessels, as a result of which it develops.
In particular, an increased level of glucose enters the blood from the liver, which is formed due to glycogenolysis and gluconeogenesis.
With insulin resistance in a patient, an increased level of the hormone insulin has been observed in the blood for many years. If a person at this moment can lead to the fact that the patient may develop type 2 diabetes mellitus.
After some time, the cells of the pancreas cease to cope with such a load, the level of which is increased many times over. As a result, the body begins to produce less insulin, which leads to diabetes. To prevent this from happening, it is necessary to start the prevention and treatment of the disease as early as possible.
Cardiovascular disease in insulin resistance
As you know, in people with diabetes, the risk of early death increases several times. According to doctors, insulin resistance and hyperinsulinemia are the main serious risk factors for stroke and heart attack. It does not matter if the patient has diabetes.
Elevated insulin negatively affects the condition of blood vessels, leading to their narrowing and the appearance of atherosclerotic plaques. Including the hormone promotes the growth of smooth muscle cells and fibroblasts.
Thus, hyperinsulinemia becomes one of the main causes of atherosclerosis. Symptoms of this disease are detected long before the development of diabetes.
A major link between excess insulin and the development of cardiovascular disease can be identified. The fact is that insulin resistance contributes to:
- increased abdominal obesity;
- deterioration of the blood cholesterol profile, due to which cholesterol plaques appear on the walls of blood vessels;
- increase the likelihood of blood clots in the blood vessels;
- thickening of the wall of the carotid artery, which leads to a narrowing of the lumen of the artery.
These factors can occur both in type 2 diabetes mellitus and in its absence. For this reason, the sooner the patient begins treatment, the more likely it is. that there will be no complications.
If there are signs of insulin resistance, treatment is with a therapeutic diet that restricts carbohydrate intake. This helps to control and restore balance in case of metabolic disorders in the body. Such a diet is introduced both in diabetes mellitus and in its absence. At the same time, such a menu in daily nutrition should become the main one throughout life.
After treatment with a therapeutic diet begins, the patient will begin to feel better after three to four days. Including in a week they are normalized.
After six to eight weeks, with proper nutrition, tests usually report an increase in good cholesterol and a decrease in bad cholesterol. As a result, the risk of developing atherosclerosis is reduced.
One of the factors leading to the development of diabetes mellitus, cardiovascular disease and the formation of blood clots is insulin resistance. It can be determined only with the help of blood tests, which have to be taken regularly, and if you suspect this disease, you must constantly be monitored by a doctor.
The concept of insulin resistance and the causes of its development
This is a reduced sensitivity of cells to the action of the hormone insulin, regardless of where it comes from - produced by the pancreas or injected.
An increased concentration of insulin is detected in the blood, which contributes to the development of depression, chronic fatigue, increased appetite, obesity, type 2 diabetes, and atherosclerosis. It turns out a vicious circle, leading to a number of serious diseases.
Reasons for the development of the disease:
- genetic predisposition;
- hormonal imbalance;
- malnutrition, eating a large amount of carbohydrate food;
- taking certain medications.
At the physiological level, insulin resistance appears as a result of the fact that the body suppresses the production of glucose, stimulates its uptake by peripheral tissues. In healthy people, muscles utilize 80% of glucose, therefore, it is as a result of incorrect work of muscle tissue that insulin resistance occurs.
Based on the following table, you can find out who is at risk:
Symptoms of the disease
An accurate diagnosis can only be made by a specialist based on the results of the analysis and observation of the patient's condition. But there are a number of alarm signals that the body gives. In no case should they be ignored, and as soon as possible, you should consult a doctor for an accurate diagnosis.
So, among the main symptoms of the disease can be identified:
- distracted attention;
- frequent flatulence;
- drowsiness after eating;
- changes in blood pressure, often there is hypertension (high blood pressure);
- obesity in the waist is one of the main signs of insulin resistance. Insulin blocks the breakdown of adipose tissue, so losing weight on various diets with all the desire does not work;
- depressive state;
- increased feeling of hunger.
When passing tests, deviations such as:
- protein in the urine;
- elevated triglycerides;
- elevated blood glucose levels;
- bad cholesterol tests.
When taking an analysis for cholesterol, it is necessary to check not its general analysis, but separately the indicators of “good” and “bad”.
A low level of "good" cholesterol can signal an increased resistance of the body to insulin.
Analysis for insulin resistance
The delivery of a simple analysis will not show an accurate picture, the level of insulin is a variable value and changes during the day. A normal indicator is the amount of hormone in the blood from 3 to 28 µU/ml if the analysis was taken on an empty stomach. With an indicator above the norm, we can talk about hyperinsulinism, that is, an increased concentration of the hormone insulin in the blood, resulting in a decrease in blood sugar levels.
The most accurate and reliable is the clamp test or euglycemic hyperinsulinemic clamp. It will not only quantify insulin resistance, but also determine the cause of the development of the disease. However, it is practically not used in clinical practice, as it is laborious and requires additional equipment and specially trained personnel.
Insulin Resistance Index (HOMA-IR)
Its indicator is used as an additional diagnosis to detect the disease. The index is calculated after passing a venous blood test for insulin and fasting sugar levels.
Two tests are used in the calculation:
- IR index (HOMA IR) - the indicator is normal if less than 2.7;
- insulin resistance index (CARO) - is normal if below 0.33.
Indices are calculated according to the formulas:

In doing so, the following must be taken into account:
- IRI - immunoreactive insulin on an empty stomach;
- GPN - fasting plasma glucose.
If the index is above the norm, the indices indicate an increase in the body's resistance to insulin.
For a more accurate analysis result, you must follow a few rules before taking the analysis:
- Stop eating 8-12 hours before the test.
- The analysis is recommended to be carried out in the morning on an empty stomach.
- When taking any medications, you must inform your doctor. They can greatly affect the overall picture of the analysis.
- Do not smoke half an hour before donating blood. It is advisable to avoid physical and emotional stress.
If, after passing the tests, the indicators turned out to be above the norm, this may indicate the course of such diseases in the body as:
- type 2 diabetes;
- cardiovascular diseases, for example, ischemic heart disease;
- oncology;
- infectious diseases;
- gestational diabetes;
- obesity;
- polycystic ovary syndrome;
- pathology of the adrenal glands and chronic renal failure;
- chronic viral hepatitis;
- fatty hepatosis.
Can insulin resistance be cured?
To date, there is no clear strategy that would cure this disease completely. But there are tools that help in the fight against the disease. It:
- Diet . Reduce the intake of carbohydrates, thereby reducing the release of insulin.
- Physical exercise . Up to 80% of insulin receptors are located in the muscles. Muscle work stimulates the work of receptors.
- Weight loss . According to scientists, with a weight loss of 7%, the course of the disease improves significantly and a positive prognosis is given.
The doctor can also individually prescribe pharmaceutical drugs to the patient to help with the fight against obesity.
With an increased rate of the hormone in the blood, they follow a diet that is aimed at helping to stabilize its level. Since the production of insulin is the body's response to an increase in blood sugar, sharp fluctuations in blood glucose should not be allowed.

Basic diet rules
- Exclude from the diet all foods with a high glycemic index (wheat flour, granulated sugar, pastries, sweets and starchy foods). These are easily digestible carbohydrates that cause a sharp jump in glucose.
- When choosing carbohydrate foods, the choice is stopped at foods with a low glycemic index. They are more slowly absorbed by the body, and glucose enters the bloodstream gradually. And also preference is given to foods rich in fiber.
- Introduce foods rich in polyunsaturated fats into the menu, reduce monounsaturated fats. The source of the latter are vegetable oils - linseed, olive and avocado. Sample menu for diabetics -.
- Restrictions are being introduced on the use of high-fat foods (pork, lamb, cream, butter).
- More often they cook fish - salmon, pink salmon, sardines, trout, salmon. Fish is rich in omega-3 fatty acids, which improve the sensitivity of cells to the hormone.
- You can not allow a strong feeling of hunger. In this case, there is a low level of sugar, leading to the development of hypoglycemia.
- You need to eat in small portions every 2-3 hours.
- Observe the drinking regime. The recommended volume of water is 3 liters per day.
- Give up bad habits - alcohol and smoking. Smoking slows down metabolic processes in the body, and alcohol has a high glycemic index (more about alcohol - diabetic.
Additives
Additionally, mineral supplements are introduced:
- Magnesium . Scientists have conducted research and found that increased levels of the hormone and glucose in the blood of people with a low content of this element, so the lack needs to be filled.
- Chromium . The mineral stabilizes blood glucose levels, helps process sugar and burn fat in the body.
- Alpha Lipoic Acid . An antioxidant that increases the sensitivity of cells to insulin.
- Coenzyme Q10 . Strong antioxidant. It must be consumed with fatty foods, as it is better absorbed. Helps prevent the oxidation of "bad" cholesterol and improves heart health.
Sample menu for insulin resistance
There are several menu options for insulin resistance. For example:
- Start the morning with a serving of oatmeal, low-fat cottage cheese and half a glass of wild berries.
- Snack on citrus fruits.
- Lunch consists of a portion of stewed white chicken meat or oily fish. For garnish - a small plate of buckwheat or beans. Vegetable salad of fresh vegetables flavored with olive oil, as well as a small amount of spinach or lettuce greens.
- They eat one apple for lunch.
- For the evening meal, they prepare a portion of brown rice, a small piece of stewed chicken or fish, fresh vegetables, poured with oil.
- Before going to bed, have a snack with a handful of walnuts or almonds.

Or another menu option:
- For breakfast, milk unsweetened buckwheat porridge with a small piece of butter, tea without sugar, crackers are prepared.
- Lunch is baked apples.
- For lunch, they cook any vegetable soup or soup in a weak meat broth, steamed cutlets, stewed or baked vegetables, dried fruit compote for a side dish.
- For an afternoon snack, it is enough to drink a glass of kefir, fermented baked milk with diet cookies.
- For dinner - brown rice with stewed fish, vegetable salad.

Do not forget about the list of foods that diabetics should not. Under no circumstances should they be used!
Insulin resistance and pregnancy
If a pregnant woman is diagnosed with insulin resistance, it is necessary to follow all the doctor's recommendations and fight excess weight by watching nutrition and leading an active lifestyle. It is necessary to completely abandon carbohydrates, consume mainly proteins, walk more and engage in aerobic training.
If left untreated, insulin resistance can cause cardiovascular disease and type 2 diabetes in the mother-to-be.
Minestrone Vegetable Soup Video Recipe
In the following video, you can see a simple vegetable soup recipe that can be included in the menu for insulin resistance:
If you strictly adhere to the diet, lead an active lifestyle, the weight will gradually begin to decrease, and the amount of insulin will stabilize. The diet forms healthy eating habits, therefore, the risk of developing dangerous diseases for humans - diabetes mellitus, atherosclerosis, hypertension and cardiovascular diseases (stroke, heart attack) is reduced, and the overall condition of the body improves.
About insulin resistance and its characteristic features on the site was discussed many times. And there was no information about what it should be. So, from this material you will learn:
- how to learn about insulin resistance;
- why insulin resistance needs to be eliminated;
- what diseases are associated with this pathology;
- about changes in tissues and organs in the event of insulin resistance;
- about the principles of nutrition and diet for insulin resistance.
How do you know if you have insulin resistance?
Very often, patients ask: "how do I know that I have insulin resistance?". To answer this question, you need to turn to the help of mathematics. In other words, you need to use a simple formula that characterizes the HOMA index.
So, to assess the presence of insulin resistance, a study of the level of insulin and glucose on an empty stomach is carried out (a prerequisite: overnight fasting for at least 8 hours). Based on the results obtained, the calculation index HOMA-IR is calculated:

If the level of fasting insulin or glucose is high, the HOMA index rises accordingly. For example, if the fasting glucose level is 7.2 mmol / l, and insulin is 18 μU / ml, the HOMA index will be 5.76. The norm for this index is considered to be below 2.7.
In addition, a decrease in tissue sensitivity to insulin can be assessed by the Caro index:
Caro = serum glucose/serum insulin.
A result below 0.33 indicates the presence of resistance.
Why fight insulin resistance?
To date, a decrease in the sensitivity of tissues to one of the most important hormones of the endocrine apparatus - insulin, occurs in a fairly large number of people who, by the way, may not even be aware of it. Nevertheless, the long-term "existence" of insulin resistance is fraught with the development of the most dangerous diseases, including atherosclerosis, diabetes mellitus, etc.
Let's try to explain briefly: the human body, trying to help overcome the existing insensitivity of surrounding tissues to insulin and increase the degree of absorption of glucose by cells, compensatory increases the synthesis of the hormone by islet cells of the gland. In his goal to eliminate the deficiency of insulin action, in reality the situation is even more complicated ...
Naturally, hyperinsulinemia (a high level of this hormone in the blood) that occurs against the background of connected compensatory mechanisms cannot overcome insulin resistance. As a result, hyperinsulinemia is observed in most patients with reduced sensitivity to the action of insulin.
And if such a patient also suffers from diabetes, the body practically works "for wear and tear", and it is not surprising that after a short period of time problems with certain organs and systems appear.
Diseases associated with insulin resistance
Below we list the diseases and conditions that are somehow associated with this pathology, and accompany it most often:
- ischemic disease;
- obesity;
- hypertonic disease;
- hyperprolactinemic hypogonadism;
- chronic foci of inflammation;
- Alzheimer's disease;
- erectile dysfunction;
- atherosclerosis;
- growth disorder;
- fatty degeneration of the liver;
- aging;
- chronic stress.
Effects of insulin resistance on organs
Unfortunately, reduced insulin sensitivity very often causes the development of arterial hypertension. This fact was proved by scientists relatively recently. If diabetes mellitus and retinopathy are added to this process, then the situation is even more aggravated.
An increase in insulin in the blood serum contributes to the activation of the process of transformation into glucose fats. The result of this process is the appearance of overweight or even obesity.
It is known that one of the main functions of insulin is to enhance the utilization of glucose by the muscles, which ensures their normal functioning. With insulin resistance, this process is disturbed, which is manifested by a decrease in the efficiency, functioning and endurance of muscle tissue.
Under the action of insulin, there is a decrease in the synthesis of glucose by the liver tissue, which is accompanied by a decrease in excessively high levels of glucose in the blood. When resistance occurs, this process is also disrupted.
Glucose is the main fuel of the body, and especially brain tissue. Making up only 6% of the total weight, the brain is able to utilize up to 20% of the glucose circulating in the blood. Insulin is involved in the control of glucose metabolism in brain tissue. It is known that with insulin resistance, neurodegenerative processes occur, for example, Alzheimer's disease.
As shown by the results of studies, there is a high level of relationship between the development of heart failure and hyperinsulinemia.
Diet for insulin resistance
And now it's time to talk about "the most important thing." Let's figure out together which foods are allowed and which are not in the presence of insulin resistance ...
This is necessary in order to facilitate for your body the process of processing carbohydrates, which we use for anyone, because they are simply necessary for normal life! According to the facts, the absolute exclusion from the diet of carbohydrate foods can lead to the development of intestinal dysbiosis and ketosis.
The main principle of the diet for insulin resistance is the complete exclusion from the diet of white flour, sugar and starch. It is important to limit the intake of easily digestible carbohydrates (jams, preserves, refined sugar, sweets, fruit juices, etc.). The diet should be rich in unsaturated fats and fiber.
The first two weeks of being on a diet, it is necessary to completely exclude certain foods from the diet in order to somewhat calm the pancreas that is working at an accelerated pace.
So, list of allowed products for the current period: cabbage (any variety), shrimp, mushrooms, yogurt, cheeses, eggs, fish, vinegar, all green vegetables, asparagus and green beans, tomatoes, lettuce, avocado, artichoke, lentils, garlic, olives, alfalfa sprouts , radish, Jerusalem artichoke, sugar-free rhubarb, zucchini, shallots, sprouted rye grains, bell pepper, green peas, avocado, blueberry, lemon, elderberry, raspberry, papaya, nectarine, sea buckthorn, green pear, coconut, cranberry, red currant , medlar, quince, pistachios, Brazil nuts, pine nuts, almonds, peanuts, pumpkin seeds, hazelnuts, peanut butter. cashew nuts. From drinks you can drink coffee without sugar, tea, water, sauerkraut juice.
It is undesirable to use: grapefruit, pomegranate, mango, peach (except nectarine), blackcurrant, plums, mulberries, kiwi, gooseberries, fresh figs, dried apricots, green apples, strawberries, acerola, raisins, oranges, tangerines, apricots, pineapple, liver, milk, oysters , white beans, new potatoes, carrots, corn, dandelion, couscous, chestnuts, onions, parsnips, beets, fruit bread, rye bread, pasta, whole grain bread, black bitter chocolate, cereals (any). From drinks, cocoa and various compotes are undesirable.
REMEMBER!
If you have already decided to use beets, onions or carrots at this stage, then be sure to process them thermally.
Foods that should not be consumed when following a diet with insulin resistance: pita bread, millet, pearl barley, chips, white bread, starch, sugar, barley, corn flakes, barley bread, sweet cherry, banana, tapioca, coconut oil, canned berries and fruits, caramel, jam, halva, cookies , lollipops, sweets, honey, ketchup, puddings, breadcrumbs, fish sticks. from drinks you can not use Coca-Cola, coffee with condensed milk, mulled wine, sherry brandy, champagne, sweet wines and liqueurs, beer, nectars and juices.
Some doctors prescribe metformin tablets to their patients when insulin resistance is detected. This therapy can be carried out on a par with the specified diet.
Leave a comment and get a GIFT!
With a violation of glucose metabolism in the body, the so-called insulin resistance develops: what is it and why does such a pathology develop? The first step is to point out that such a pathology most often occurs in patients with diabetes mellitus, and even overweight (fatty tissue in the abdomen and causes similar symptoms). However, this is not the only reason, so a comprehensive examination is indispensable.
What is insulin resistance?
As you know, the processing of sugar in the blood begins after the insulin-responsive hormone sends a command to the brain that it is necessary to start processing sugar into glucose in order to transport it to the cells (they, in turn, absorb it as energy) . However, if the signal to the brain is not received, then the very glucose metabolism is disrupted, after which the entire body ceases to function normally. Surprisingly, such a failure can initially proceed without symptoms at all, but after all this, type 2 diabetes can develop.
Symptomatically, insulin resistance can be similar to the banal excess of the permissible level of sugar in the blood. However, you need to understand that such a violation is due to the fact that the body simply stops processing glucose and absorbing it. The first symptom is a sharp deterioration in the patient's physical activity, after which a complex metabolic disorder may develop (improper absorption of glucose necessarily affects the process of processing "heavy" fats).
Insulin resistance will be most dangerous when combined with too high blood pressure. It must be understood that this is an accompanying symptom, that is, it will necessarily occur in the absence of proper treatment. Another question is when.

Reasons for developing insulin resistance
In most cases, insulin resistance is a hereditary factor, much less often - obtained during life (with numerous metabolic disorders). That is, if your close relatives had a similar violation, then with a probability of 40% this will also happen to you.
Other risk factors include those patients who:
- abuse alcohol;
- have too much excessive weight (namely in the abdomen);
- do not follow normal treatment in the presence of diabetes;
- sedentary (have a profession, for the most part associated with mental activity).
At the same time, doctors argue that insulin resistance can develop in patients with problems in the functioning of the cardiovascular system, in particular, the multiple appearance of blood clots in the vessels. All this directly or indirectly acts depressingly on the work of the liver, which ceases to lower the level of glucose normally.


Consequences of impaired glucose metabolism
In most cases, insulin resistance leads to disruption of the cardiac and reproductive systems. Recently, doctors have pointed out that such a disease can lead to the development of Alzheimer's disease, ovarian sclerocystosis, and impotence (in women and men, respectively).
In addition, initially, when the body itself tries to resume signaling (producing significantly more insulin), the disease does not manifest itself in any way. However, after some time, when the thyroid gland can no longer cope with the production of a sufficient amount of hormones, a massive metabolic failure occurs. And, as a rule, only then do doctors find all the signs of diabetes.

Diagnostics
It is believed that the index of insulin resistance and, accordingly, the presence of a metabolic failure is most correctly determined using the so-called clamp test (the result is the so-called HOMA index). To obtain data, you also need to take into account the level of sugar and insulin in the blood, so the doctor will definitely prescribe an analysis on an empty stomach (immediately before determining the index).
At the initial stage, the HOMA index may be normal, but at the same time, the analysis indicates a slightly elevated blood sugar level and too high insulin levels. All this indirectly indicates that the body does not properly absorb glucose, respectively, energy is practically not produced, and the nutrients remain in the blood, causing an excess.
If insulin resistance is suspected, the analysis for the HOMA index is carried out 3 days in a row (and always only on an empty stomach). After that, treatment will be prescribed based on the data obtained. The main reason for choosing a treatment method is the reason why the failure occurred.
![]()
Symptoms
The primary symptoms of insulin resistance include mental and physical fatigue, which is accompanied by overly agitated behavior. That is, despite his fatigue, the patient cannot fall asleep normally for a long time. The analysis carried out will not show any failures, except in the blood. However, even an increased dose of it will not cause the start of the sugar processing process. The reasons for this are described above - the body reacts incorrectly to the presence of insulin.
Along with mental irritability, the patient abruptly begins to gain weight (namely, fat mass), the normal functioning of the organs of the gastrointestinal tract is disturbed in him (often there is swelling). All these symptoms indicate precisely a metabolic failure, which leads to a rapid loss of appetite, problems with sleep (it is either too short or completely absent for several days, after which the patient simply “turns off”).
Another resistance can manifest itself as black acanthosis, in which black pigment spots appear on the elbows, knees, ankles (sometimes on the back of the head). This suggests that the patient develops precisely a chronic form of insulin resistance, in which subtle symptoms occur for a long time (2 or more years). It ends with a diagnosis, and if left untreated, with a fatal outcome.
Treatment and diet
Diet and sufficient mobility of the patient are the most effective methods of combating insulin resistance. However, you need to understand that they act only as a preventive measure. If the diagnosis has already been made, then the recovery process will take too much time (several years at best).
The main diet includes the replacement of simple carbohydrates (sugar and white flour) with complex ones in the form of whole grains, fruits. This is necessary so that the increase in the amount of sugar in the blood occurs gradually. At the same time, the patient must control insulin, if necessary, it is replaced by synthetic analogues, to which there is a natural reaction. That is, the first thing the body is brought back to normal.
If the visual symptoms of insulin resistance are still invisible (pale skin, black spots), then there is a high probability that only a diet will get rid of the disease. But you will have to completely abandon fast food, if necessary, lose weight (and the sooner the better).

Doctors also argue that adding mineral components to the menu can increase the sensitivity of mineral fibers to glucose, respectively, accelerate the processing of glucose (at least its upper limit, due to which the so-called hyperglycemia develops).
Together with all this, you will have to completely abandon your bad habits, in particular smoking (it suppresses the metabolic rate of all carbohydrate compounds). Drinking alcohol is also not recommended, as it inhibits the rate of utilization of glucose compounds.
By the way, based on the definition of insulin resistance, we can also mention that insulin is involved in the processing of not only sucrose, but also some other fatty compounds (in particular, beta-carotene). Therefore, when answering the question of why insulin resistance is dangerous, what it is, they must mention that the basis of the cause lies precisely in the pathological activity of the thyroid gland, due to which the body can no longer absorb nutrients normally (despite the fact that feces are in sufficient quantities stand out).
At the discretion of the doctor, various nutritional supplements and biologically active components may be included in the patient's daily menu (if the analysis indicates a lack of nutrients).
And all this is complemented by taking Metformin, one of the key drugs that is used for (reduces the amount of both the hormone and blood sugar, while being a complex medication).
At the same time, it contributes to a sharp decrease in the patient's weight.
And you need to understand that the so-called fruit diet in this case will not help, since this will also lead to the accumulation of insulin in the blood. The reaction of cells to it is in no way manifested, but the amount of sugar will not decrease.
By the way, the blueberry diet also reduces the amount of processed fatty tissue. In this case, the patient's weight decreases sharply, as does the risk of acanthosis formation.
Conclusion
Insulin resistance is such a disorder in the body, in which cells do not respond to an increase in the amount of insulin in the blood (in this case, the process of natural processing of glucose and its assimilation as clean energy should begin). The only correct way to make an accurate diagnosis is the so-called analysis for the HOMA index in combination with a study of the composition of the blood (the amount of sugar and a lot of insulin will be increased in it). The primary symptom is general weakness.
But medical treatment is not always effective. In most cases, it is possible to avoid it, but instead, various biological supplements are prescribed. And you also need to take into account that insulin resistance often causes infertility in girls and impotence in men, as it dramatically affects the hormonal system as a whole.
And some secrets...
If you have ever tried to cure DIABETES MELLITUS, then you have probably encountered the following difficulties:
- medical treatment prescribed by doctors, solving one problem creates others;
- replacement therapy drugs that enter the body from the outside help only for the time of admission;
- regular injections of insulin are not always convenient to do and in themselves they are unpleasant;
- severe restrictions that diabetes treatment sets spoil the mood and do not allow you to enjoy life
- RAPID WEIGHT SET and problems associated with obesity;
Now answer the question: Are you satisfied with this? Isn't there a self-healing mechanism in such a complex mechanism as your body? And how much money have you already "leaked" for ineffective treatment? That's right - it's time to end this! Do you agree? That is why we decided to publish the exclusive method of Elena Malysheva, in which she revealed the simple secret of fighting diabetes. Here is her method...